How to Use AI Tools to Create and Enhance Rubrics
By Lina Eskew, Senior Assistant Director of Equitable Assessment
Rubrics are powerful tools for promoting transparent and equitable assessment by clearly articulating student expectations and ensuring consistent grading. They align with frameworks such as the Transparency in Learning and Teaching (TILT) model, which emphasizes the importance of providing explicit assignment expectations to increase students' academic confidence, sense of belonging, and ability to self-regulate their learning and development.
Creating a well-structured rubric, particularly an analytical one (which breaks down expectations into specific criteria and performance levels) can be time-consuming. Generative AI (GAI) tools like Copilot (now available to the Northwestern University community with secure data storage through a Northwestern University tenant) or ChatGPT offer instructors an efficient and effective way to draft rubrics.
Identify the Criteria
Before generating a rubric, ensure you have a clear understanding of your assignment's learning outcomes. This will help generate more accurate suggestions for the criteria, which are the essential assignment components to be assessed. Clearly outlining what students should achieve, along with detailed descriptions of the knowledge, skills, or attitudes you want to assess (e.g., critical thinking, written communication), will improve the quality of the AI-generated rubric criteria.
Ask AI: "Help me create a rubric for an undergraduate capstone paper in Latin American history with a learning outcome focused on critical thinking." Alternatively, you could ask a broader question such as: “What key criteria should I consider when creating a rubric to assess critical thinking at the college level?”
Customize Performance Levels
Analytical rubrics typically include multiple performance levels that measure either frequency (e.g., "Always," "Sometimes") or quality (e.g., "Excellent," "Needs Improvement"). AI can help differentiate performance levels for each criterion, giving you descriptors that can be tailored to your specific assignment assessment.
Ask AI: Use a prompt like: "Can you create a rubric for an assignment on the hero's journey, with a learning outcome that focuses on creative writing, using five performance levels: Exceeds Expectations, Meets Expectations, Somewhat Meets Expectations, Does Not Meet Expectations, and No Evidence Provided?" AI will provide performance descriptors, which you can modify as needed.
Ensure Clarity
Rubrics need to be explicit and aligned with the learning outcomes of the assignment. If your rubric’s language seems unclear, AI can help simplify it to ensure students understand the expectations.
Ask AI: "Simplify the performance levels to make it clearer for first-year college students." The tool will return a more concise, student-friendly version.
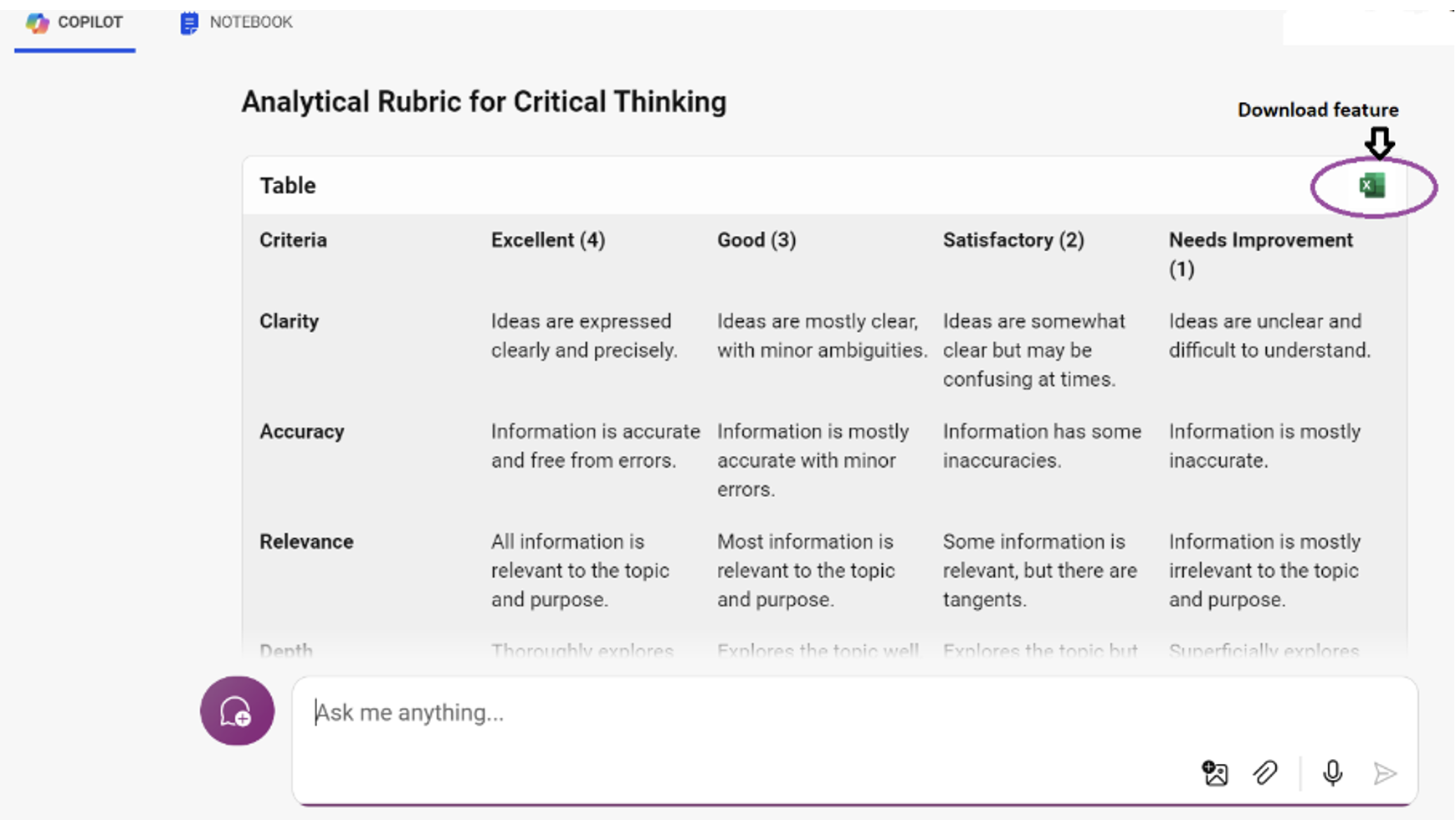
Pro Tip: You can ask AI to combine the criteria and performance levels it generates to create a template-ready rubric that is downloadable. In Copilot, there's a feature that allows you to export the template into Excel by simply clicking the download button, as shown in the screenshot. This removes the need for copying, pasting, and manual rubric formatting.
Ask for Student Feedback
While AI-generated rubrics provide a strong starting point, it’s essential to review and adjust the output to meet the specific needs of your assignment and students. Once finalized, share the rubric with students before the assignment to promote transparency and equity in the assessment process. Adjust any areas of the rubric that may be unclear to your students. Keep in mind that designing a rubric is often an iterative process, especially when trying it for the first time.
Conclusion
Using AI tools like Copilot or ChatGPT can help instructors save time and develop rubrics that are well-aligned with transparency frameworks in assessment. While it's important to review AI-generated rubrics for nuances, these tools provide a strong starting point for creating analytical rubrics.
This article was developed with assistance from ChatGPT for idea generation and prompt formulation. While AI contributed to the drafting process, the final content reflects the expertise of the author.
Published Fall 2024